The Bill of Rights 10 Amendments: Discover how the Bill of Rights protects American freedoms and shapes modern democracy. Learn its significance, real-world examples, and its enduring impact on U.S. citizens.
Introduction
Did you know that the Bill of Rights was ratified over 230 years ago but remains the cornerstone of American democracy today? As I was diving into this topic, I realized just how much these ten amendments protect our everyday freedoms—from the right to speak our minds to the assurance of fair trials. In this article, we’ll explore how the Bill of Rights continues to influence our lives in 2025, backed by real-world examples and insights into its lasting importance. Whether you’re a student, a history buff, or someone curious about your rights, this is a must-read!
Understanding the Bill of Rights 10 Amendments
1. What Is the Bill of Rights?
- Brief history: Adopted in 1791 as the first 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution.
- Purpose: To protect individual freedoms and limit government power.
- Why it was necessary: Lessons learned from British rule and the push for guaranteed rights.
2. Key Protections Offered by the Bill of Rights
- Freedom of Speech and Religion (First Amendment): Real-life cases, like protecting social media posts or religious gatherings.
- Right to Bear Arms (Second Amendment): How this amendment sparks debates in the 21st century.
- Rights of the Accused (Fifth and Sixth Amendments): Examples of fair trials and protections against self-incrimination.
- Protection Against Cruel Punishment (Eighth Amendment): How it safeguards individuals from extreme penalties.
3. How the Bill of Rights Shapes Modern Life
- Influence on education: Promoting freedom of expression in schools.
- Impact on technology: Protecting digital privacy under the Fourth Amendment.
- Everyday examples: Standing up for free speech at protests or ensuring fairness in criminal cases.
4. Challenges to the Bill of Rights in 2025
- Balancing rights and public safety in a digital age.
- Current debates: Gun control, surveillance, and freedom of the press.
- Court cases shaping interpretations: Insights into recent landmark decisions.
5. Why Understanding the Bill of Rights Matters Today
- Helps you protect your rights in daily life.
- Encourages civic engagement: Voting, protesting, and advocacy.
- Connects history to the present: Why these amendments are still relevant in 2025.
Bill of Rights: Understanding the First 10 Amendments
The Bill of Rights is one of the most significant documents in American history. It lays the foundation for the freedoms and rights citizens enjoy today. Let’s explore the key aspects of the Bill of Rights, its importance, and the details of its amendments.
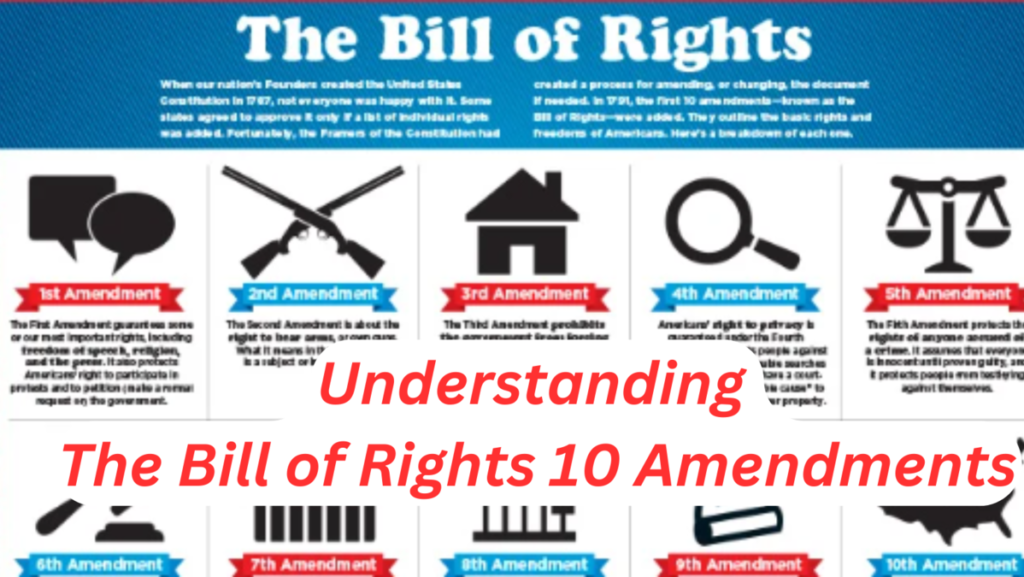
What Are the 10 Amendments in the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights comprises the first 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution, each protecting specific individual freedoms and limiting government power:
- First Amendment: Freedom of religion, speech, press, assembly, and petition.
- Second Amendment: The right to bear arms.
- Third Amendment: Protection from quartering of troops.
- Fourth Amendment: Protection against unreasonable searches and seizures.
- Fifth Amendment: Rights in criminal cases, including protection against self-incrimination and double jeopardy.
- Sixth Amendment: Right to a speedy and public trial by an impartial jury.
- Seventh Amendment: Right to a trial by jury in civil cases.
- Eighth Amendment: Protection against excessive bail, fines, and cruel or unusual punishment.
- Ninth Amendment: Acknowledgment that other rights exist beyond those listed in the Constitution.
- Tenth Amendment: Powers not delegated to the federal government are reserved for the states or the people.
Why Is the Bill of Rights Important?
The Bill of Rights ensures that the government cannot infringe upon the fundamental rights of its citizens. Here’s why it matters:
- Protects Individual Liberties: It guarantees freedoms like speech, religion, and the press.
- Limits Government Power: By outlining specific rights, it prevents government overreach.
- Guides Legal Interpretations: Courts use it to resolve disputes and safeguard rights.
- Maintains Democracy: It empowers citizens to challenge unjust laws or practices.
Example: The First Amendment protects the right to peaceful protest, a cornerstone of democratic expression in modern times.
Who Wrote the Bill of Rights?
The Bill of Rights was drafted by James Madison, who is often called the “Father of the Constitution.” Madison introduced these amendments to Congress in 1789 to address the demands of Anti-Federalists who feared federal government overreach.
Bill of Rights List and 10 Amendments in Order
To understand the significance of each amendment, here they are in order:
- First Amendment: Freedoms of religion, speech, and press.
- Second Amendment: Right to bear arms.
- Third Amendment: No quartering of soldiers.
- Fourth Amendment: Protection against searches and seizures.
- Fifth Amendment: Rights in criminal cases.
- Sixth Amendment: Speedy trial rights.
- Seventh Amendment: Civil jury trials.
- Eighth Amendment: No cruel punishment.
- Ninth Amendment: Unenumerated rights.
- Tenth Amendment: States’ rights.
Bill of Rights Summary
The Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution to address concerns that individual freedoms might not be protected adequately. It balances power between the government and the people by enumerating key rights and freedoms. Each amendment serves as a safeguard against tyranny.
Bill of Rights PDF
Looking for a handy reference? Many resources offer the Bill of Rights in PDF format, making it easy to access on the go. Search for a reliable government or educational site to download a free copy of the Bill of Rights.
Conclusion
The Bill of Rights isn’t just a relic of history; it’s a living document that continues to shape our freedoms every day. When I reflect on its influence, I’m amazed at how it empowers individuals to stand up for what’s right and ensures justice is served fairly. Whether you’re defending free speech or advocating for privacy, understanding these amendments equips you to navigate the challenges of modern life. So, what steps will you take today to uphold the rights that protect us all?